The recent battles between the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF), which owns the Amul brand, and Nandini in Karnataka and Aavin in Tamil Nadu may have some roots in a 10-year-old headline-grabbing tussle between Verghese Kurien, the driving force behind India’s White Revolution and GCMMF chairman, and Amrita Patel, chairman of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
Patel, a Verghese protégé, had wanted to create and umbrella brand under Mother Dairy (an NDDB subsidiary), by setting up joint ventures with state federations to create a centralised brand. Mother Dairy would hold a 51 percent stake in each joint venture. Kurien resisted fierecely on grounds that it would corporatize the dairy sector. After several rounds of truce talks, in which even the then deputy prime minister L K Advani had to intervene, Patel’s plant was shelved.

That episode may well have created an aversion to centralization in the cooperative dairy sector- hence Nandini and Aavin’s reluctance to tie up with Amul. Moreover, the cooperative sector dynamics have changed since 2003. When Kurien resigned from GCMMF in 2006, it was a Rs. 3,600 – crore federation. Now Amul is India’s largest FMCG brand with a reported group turnover of Rs. 72,000 crore in 2022-23, Naturally, it has the money power to compete against any state cooperative.
The current controversy started in December last year, when Union Home and Cooperation Minister Amit Shah said, “Cooperation between Amul and Nandini can do wonders in the dairy sector.” Opposition parties in the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) ruled state immediately saw in this a move to merge the Rs. 21,000 crore Nandini with Gujarat-based Amul.
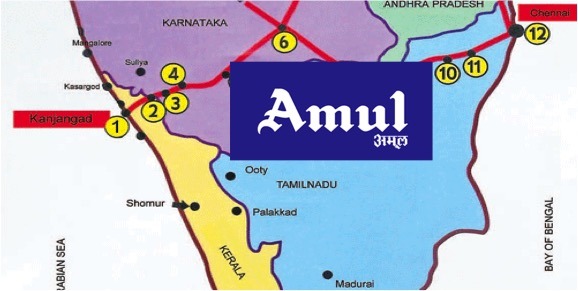
In April, in the middle of the Assembly election campaign, Amul announced that it would enter Karnataka to supply milk and curd. This led to widespread protests across the state, providing the Congress with a handy issue to mobilise pro-Kannada sentiments. A recent change in the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, making the merger of two state cooperative easier, fuelled the Opposition’s argument.
On May 25, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M K Stalin approached Shah, seeking his intervention to direct Amul to desist from milk procurement from the milk shed catchment area of Aavin (the Tamil Nadu Co-operative Milk Producers Federation) in his state with immediate effect.
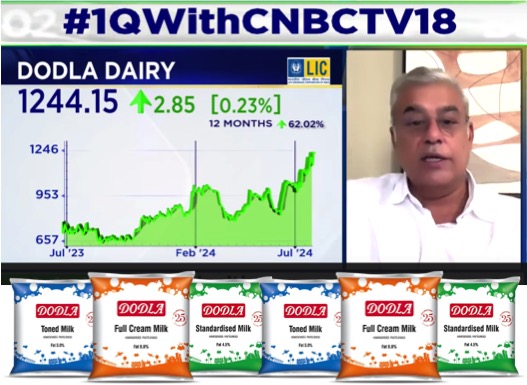
Though Nandini and Aavin are small brands compared to Amul, they have a strong market presence in their respective state. Nandini, owned by the Karnataka Milk Federation, produces over 9 million liters of milk per day and has 2.64 million members dependent on it. Meanwhile, Aavin procures 3.5 million liters per day with around 450,000 members for 2022-23 show that it has 3.6 million registered members and procures an average of 27 million liters per day.
What is more, Amul products were already being sold in both states. So what was the problem? “As long as Amul was coming in with products it was not a problem because it was something value added and with a shelf life. When it gets into the local market by procuring locally, it cuts into the market share of local cooperative. This choking in procurement itself may hit the rest of the value chain of the local cooperative, “ M S Sriram, a professor at the Centre for Public Policy, Indian Institute of Management- Bangalore, told Business Standard.
But a senior industry official and a long-timer with Amul said, nobody could stop Amul from entering into procurement tie-ups leagally, because “it is not creating new members, which it cannot do being a state cooperative registered under the state laws”. In fact, he added, Amul currently procures milk in 10 or 12 states apart form Gujarat, including uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, Rajasthan, Punjab, and West Bengal, either on its own or through local cooperatives.
“To me it’s a win-win situation because Amul will pay a higher and better price to farmers for their milk, consumers will get cheaper milk products and it is also good for the dairy industry,
“ he said. He added that as more organized players entered the market, it would bring transparency in operations and pricing and also benefit consumers, “More buyers means a better price of the milk for farmers, “the official said. “ In some states, even the state governments invite Amul to set up its own procurement and chilling centres to help milk farmers.
But, critics say that Amul’s foray is welcome in those state where the cooperative structure is weak, but in southern states, where milk cooperatives are big and strong, such creeping entry has stared creating problems.
To those who pitch argument and the portrayal of Amul a cooperative, Sriram has a counter view. “When it comes to other states, Amul is not a cooperative, because it is a cooperative of the farmers of Gujarat and accountable to the farmers of Gujarat and not to the farmers of Karnataka or Tamil Nady, even if they procure from them, “he said. As he wrote in an article in The Wire, other strong local brands lost our in Gujarat when Amul was given prominence – Sagar by Dudhsagar Dairy in Mehsana, Sugam in Vadodara, Sumil from Surat and, Vasundhara from Valsad.
Another major argument put forward by those supporting Amul entry is that the private sector is also procuring milk from these states. But the fact is that the private sector’s market share in liquid milk is much lower. The reason several experts do not think competition in milk procurement is good is the structure of the milk value chain. Milk has to be procured from villages and then transported and processed at the nearest plant. “That means that procurement has to be monopolistic in nature. It becomes unviable for the other players if they are unable to procure milk. Amul has deep pockets and can bleed for a while and sustain such operations, “Sriram told Business Standard.
Interestingly, according to the Amul website, it has plants in Gujarat, Delhi/NCR region, UP, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Jammu & Kashmir, and Jharkhand, but no plants in South India, indicating that the region is still a roadblock for the mega player. Whether Amul becomes a pan-Indian brand or not is a pure business decision. However, experts indicate that the move may deviate from Kurien’s dream of having hundred Amul- like brands in India.